The reasons for this are numerous, increasing average age of nurses, increasing average weight of average patient, and a nationwide shortage of nursing professionals.
Overall, the lateral transfer accounts for approximately 50 per cent of injuries suffered by healthcare workers. This is a figure that CAN be reduced through the proper use of innovative safety equipment that helps reduce/eliminate lateral transfers. Combine this with proper education and training, and the risk of nurses injury to transfers can be reduced greatly, if not eliminated.
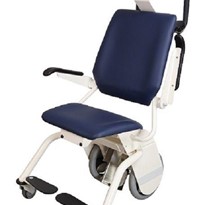
The state-of-the-art TransMotion Medical TMM3 was piloted at this hospital and the TransMotion Medical Video-Fluoroscopy Chair is regarded as a means to reduce the total number of lateral transfers at this facility. This report combines the research available on injuries and proper usage of the TMM3 Video Fluoroscopy Chair as recommended by TransMotion Medical Inc. All of this information is compiled into this report.
Background/evidence:
Healthcare is reaching a critical state to address the injuries being suffered by nurses.
According to the June 19, 2006 issue of Nurse Week, these are the most current statistics from the American Nurses Association (ANA):
- 52 per cent of nurses complain of chronic back pain;
- 12 per cent leave the profession, citing back pain as a major factor
- 20 per cent transfer to a different unit, out of direct care, or to other employment because of back problems or neck problems and shoulder injuries
"Nursing is ranked second only to industrial work for physical workload intensity and is a high risk profession for back injury." (Engles, Landeweerd, & Kant, 1994; Kjellberg, Johnsson, Proper, Olsson, & Hagberg, 2000; Skovron, Nordin, Sterling & Mulvihill, 1987).
Compared with the general working population, nurses have a considerably higher prevalence and incidence of back pain and back injuries (Hignett, 1996; Kjellberg et al., 2000; Smedley, Egger, Cooper & Coggon, 1997). Pheasant and Stubbs (1992) reported that nurses have approximately 30 per cent more days off due to back pain compared with only 8 per cent in the general working population.
Key risk factors included excessive physical workload, low job satisfaction, history of back injury, age, lack of sports activities, and night shift work (Elfering et al., 2002; Nordin & Frankel, 1980) Yassi et al. (1995) found that lifting and transferring patients were the two most common mechanisms for back injury among nurses.
Stubbs and Buckle (1984) found that 36 per cent of all low back pain in nurses was associated with patient handling. This confirms a study by Jensen (1990) that found that the prevalence rate of back injuries among nurses who frequently handled patients was 3.7 times that of those who infrequently handled patients.
Discussion of TransMotion Medical Video Fluoroscopy Chair:
Correctly used, the TMM3 has the ability to reduce patient transfers by approximately 50 per cent of the total transfers now required for the modified barium swallow study. Patient transfers present a risk to the patient, and an increasing risk to the healthcare worker. The TMM3 is capable of reducing total transfers by the following:
Before TransMotion Medical TMM3:
Patients are transferred from Bed to Stretcher (1 transfer) and wheeled to the Radiology Department. The patient is then transferred to the current swallow study chair (2 transfers), where the study is then performed.
Following the procedure, the patient is then transferred back to the stretcher (3 transfers), and then wheeled back to the patient room where the patient is again transferred back to their bed (4 transfers).
- Four total patient transfers per procedure
- Ten procedures per week would yield 40 patient transfers
After TransMotion Medical TMM3:
Patients are transferred from Bed to the Motorised TMM3 Video Fluoroscopy Chair (1 transfer). The motorised positioning permits effortless positioning of the TMM3 from chair to stretcher position. The patient is then wheeled to Radiology where the swallow study is performed directly on the TMM3. After the study, the patient is re-positioned to a stretcher position and able to be transferred directly back to their bed (2 transfers).
- Two total patient transfers per procedure
- Ten procedures per week would yield 20 patient transfers
- Fifty per cent reduction in total patient transfer
- Yearly reduction: 1040 transfers
The TransMotion Medical TMM3 Difference:
The Modified Barium Swallow Study can be done with less total transfers of the patient.
This allows for a safer and more comfortable experience for the patient. Further, the healthcare workers are subjected to TWO less transfers per case. This is a significant reduction in total patient transfers over the life of the TMM3 Chair.
Additionally, patients can be safely positioned using the motorised positioning during the Modified Barium Swallow Study. This allows for increased efficiency, and less time per procedure.
All of these steps are accomplished without any potential for harm to the patient, and with greatly reduced risk of injury to the healthcare worker. Current industry statistics indicate that the average workmen's comp claim costs the typical facility approximately $25,000.
Summary of implementation of the TransMotion TMM3:
According to Kim Armstrong of the Washington State Nurses Association: "proper body mechanics are taught in nursing schools, but the principles are based on the straight-up lifting of boxes."
It is common knowledge that body mechanics alone is not a solution to the need to move patients. The use of medical devices to help in the reduction of transfers is becoming the most logical and long term solution.
The risk of injury to healthcare workers can no longer be ignored. This industry has reached a critical point where this issue must be addressed. Following proper training and usage of the TMM3 Video Fluoroscopy Chair, the ability to eliminate injuries due to patient transfers can become a reality for this facility.